In today's blog, we will take a deep dive into the basic functionality of Power BI. We will talk about the types of filters available in the Power BI whether in the query editor or at the visualization level. Let's start with the purpose of using filters that is limiting the rows on the basis of a condition or restrict the data which you don't want to showcase in your visualization. There are many types of filters available in Power BI. We will start with the filters available in the query editor. I am considering the sample superstore data. So, I have imported the Orders and Returns table and we will be applying the filter on the order date.
When we select the date filters it will lead to a pop-up where you can select basic and advanced filtering currently I am selecting the advanced version. The filter will limit the data for a particular duration as you can see in the image below.
You can remove the filter just by selecting the clear filter. Just to check the code of the filter you can select the column and you can see the code.
There are many options for filters in the query editor we will now move to the visualization filters. There are mainly two filters- visual-level filters and page-level filters. As the name suggests if you apply a filter on the page level then it is applied on all the visualization available on that page whilst at the visual level you can restrict the data on that particular visual.
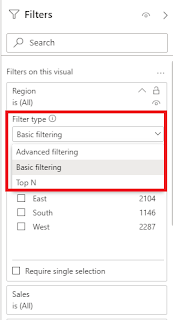
If you select the visual level filters there are 3 types associated with it one is basic filtering, advanced filtering, and top N. Basic filtering just give a simple option to restrict a particular data for example if we put a category in the filter and we only want to showcase furniture then basic filtering is a great option. When it comes to advanced filtering then it is the relative filtering based on a condition like greater than a particular number and top N provides a list of top products/categories (N represents the number).
You can apply basic or advanced filters together for different fields. For instance, we will select only the furniture category also where the profit is greater than 5000 USD and doesn't give blank values.
Now we will consider the include and exclude filters. For that, we will create a bar graph for different regions showcasing their sales. We want to exclude the west region from that graph. To do so right-click on the bar graph and you can see options for include and exclude.
There are many filters other than this but the idea of this blog is just to a gist of filters. But if you google about filters there is a common question how filters are different from a parameter? If you consider the parameter it is mainly applied to the query editor and it is an integral part of query folding so if I apply that particular parameter it will affect the dataset and hence limit the data size at the back end. It will be applied throughout your report, unlike filters which can be either applied on the page level or the visual level.
Thanks for Reading Let's connect on LinkedIn. For more such blogs do follow us.







Comments
Post a Comment