Calculated column and Measures in Power BI
This blog may seem to be very elementary but I firmly believe it is the foundation of DAX in Power BI. Our nucleus for today is Calculated columns and measures in Power BI. If you are a Power BI user you must have come across these terms. You can find both of them in the home tab (placed next to each other). We will highlight the difference between both of them and the limitations associated with them. Let's get started!!
You can easily increase the table size by adding calculated columns to it and you can provide a DAX or logic for that column. The most pivotal thing we need to be aware of such columns is that they are calculated at the row level. There are situations when you can't create a relationship between tables in such cases calculated columns can come to the rescue. But be aware that the calculated column occupies a space in the memory which can be good or bad in different scenarios. If the DAX for your calculated column is complex then it can provide you a much better experience. If you are totally relying on creating calculated columns over and over then you are increasing your table size and it doesn't fall under the good practices in Power BI.
Let's see how the calculated column works. I am considering the sample superstore data and I will be creating a column name cost which is the difference between the sales and the profit.
You can easily rename the column. One great and key learning which I came across is you can easily apply calculated columns in the page level filters but not the measures. I am creating a table that consists of an Order ID, sales, cost, and profit.
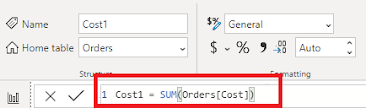
What if I don't want to calculate values on row level but I want to see the aggregated values for multiple rows? In such cases, you can use the measures. What do I mean by aggregated values so let's suppose I am writing a DAX for SUM(Orders[Cost]) so it will provide a sum for all the rows that are aggregated under this but if you use the same DAX in the calculated column it will provide you different value based on the row you are referring to.
One of the interesting and absurd facts about the measures is that you create measures inside the table but still it is not the active part of the table. So if you are looking to establish a relationship between tables with the help of measures then you can't do it.
I am creating measures in the orders table which is the sum of the cost. We will be using the same dataset for this and then we will create a card visualization that will showcase the total cost.





Comments
Post a Comment