SQL Joins
Are you aware of the fundamentals of a Set theory which entails a critical element for our database i.e. the concept of joins? Why do we need Joins in the database? Joins are the fundamental element if you want to combine various tables using a common or related column between them. Joins are mainly used in every analytical and business intelligence tool.
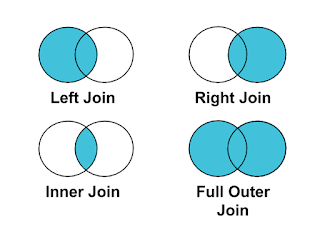
Let's take a deep dive into the fundamentals of joins which is apparent by using a Venn diagram. There are mainly four types of joins- Inner, Left, Right, and Full outer join. Let's suppose we have two datasets A and B. When we focus on inner join it basically means the focus will be on the intersection or common columns present in both datasets. Similarly, the left join focuses on the dataset that is available in A and the common columns between both data sets. Right join is quite identical to left join but the main difference is it takes the data from B along with the common columns present between both data sets. Lastly, full outer join entails the complete data present in both A and B.
This blog will mainly focus on SQL joins because that's the biggest dilemma for beginners where to use which joins when writing a query. Let's remove the dust from this first we need to get familiar with the syntax query.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
INNER/OUTER/LEFT/RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name = table2.column_name;
To configure it out you need to understand the Venn diagram that is mentioned above. Inner join is used when there is a commonality that exists between your data. Inner join identifies the data which is common and overlapping in nature. It returns the rows of data which has some exact matches. Whilst Outer join on other hand returns all rows including the ones which do not have any match or contains null values. Normally full outer join is not that popular when we consider MySQL database. An outer join will return all the data which is similar to taking a copy of the data in a common table.
There's a big question which is needed to be addressed when we talk about inner and outer joins i.e. Can we use inner and outer join in the same query? Yes, it is possible to use both in the same query but keeping their order in mind because it can be tricky at times. According to my experience if you use LeftOuter Join before applying an Inner Join then you will get the desired results but it can be false too because it depends on the data and constraints you are working with. I would recommend you to have a look at Jeff Smith Blog. It will provide you greater insight when you are using multiple joins.


This was helpful. Thanks!
ReplyDeleteThank you!! Subscribe to my blog for more articles.
ReplyDelete